What is atp in biology
How is ATP formed in cells? What type of molecule is ATP? Is ATP a high energy molecule? It is one of the most important and major energy sources of the body.

It is used in almost all the functions and is produced by two major processes: glycolysis and the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle). All living things use ATP. ATP has P's hence "Tri"-Phosphate. Adenosine Tri-Phosphate.
For the muscles, as well as all body cells, the source of energy that keeps everything workiing is called ATP. The adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the biochemical tool for storing and using energy. Hope helps, and sorry my english.
There are many similarities and differences! Oxidative Photophosphorylation: 1. Occurs during respiration 2. Utilizes oxygen for the formation of ATP Photophosphorylation: 1. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the energy-carrying molecule used in cells because it can release energy very quickly. Energy is released from ATP when the end phosphate is removed. In biology, "ATP" stands for "adenosine triphosphate".
The more energy required for a chemical reaction, the more ATP molecules must be spent. It is where our cells get the energy needed to perform their tasks.
This lesson will define ATP, explain its structure, and briefly outline how it works. ATP means adenosine tri phosphate, the energy currency of the cell. ATP are formed in mitochondria of the cells during cellular respiration.
ATP is the molecule that fuels life. The energy produced during respiration combines with ADP, adenosine di phosphate and inorganic phosphate to form ATP, which are stored in the cells as currency and are used to release energy by their breakdown when needed.
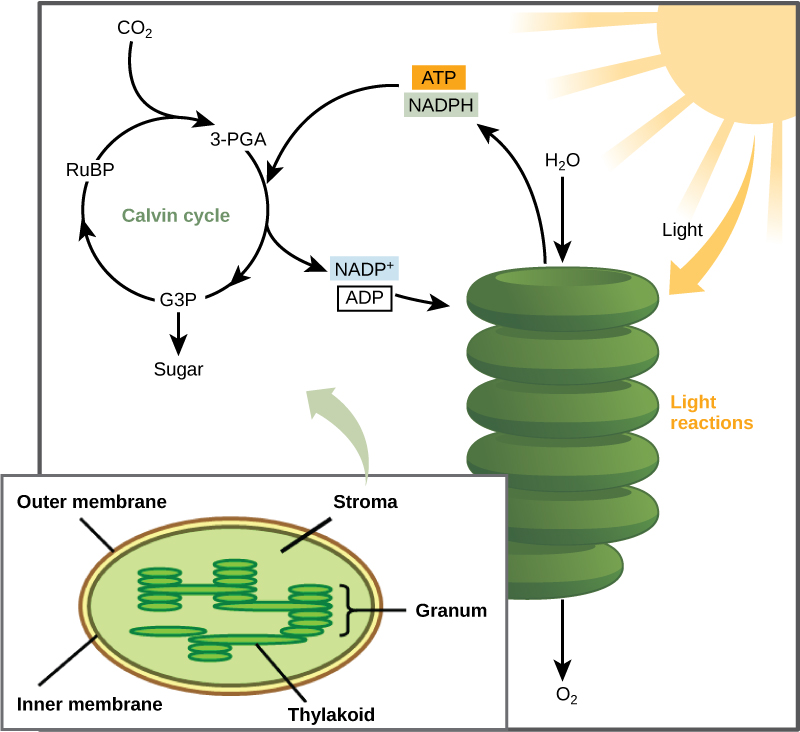
The ATP needs to be broken down to liberate its energy. This is done by an enzyme, ATPase. Hydrolysis of ATP to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and an inorganic phosphate group (P i ) is catalysed by the enzyme ATP hydrolase. It is often referred to as the energy currency of the cell and can be compared to storing.
The last two phosphates are joined by high energy bonds which provide energy used in chemical reactions such as respiration and glycolysis. It is the major energy currencyof the cell, providing the energy for most of the energy-consuming activities of the cell.
It regulates many biochemical pathways. Its job is to store and supply the cell with needed energy. Account for each ATP in the total.
The phosphate groups can be removed one at a time, releasing energy with each change in structure. This enables ATP to travel freely within the cell. It means it has a ribose as its sugar and three phosphate groups attached.
Its structure is comprised of a purine base, particularly adenine that is bound at the 9′ nitrogen atom to the 1′ carbon atom of ribose sugar, and a three phosphate groups. Below are the ways it provides energy which can described in an exam. ATP stands for a denosine t riphos p hat e, and is the energy used by an organism in its daily operations. A source of energy.
It consists of an adenosine molecule and three inorganic phosphates. After a simple reaction breaking down ATP to ADP, the energy released from the breaking of a molecular bond is the energy we use to keep ourselves alive.
Comments
Post a Comment